Key Takeaways on Benefits and Use Cases of AI in Manufacturing
- AI in manufacturing boosts operational efficiency by 50% through automated quality testing and predictive maintenance that reduces downtime by 35-45%
- Top-performing companies generate 13% ROI on AI implementations, with benefits including 25% lower maintenance costs, 15% reduced logistics costs, and 35% smaller inventory levels
- Critical applications include predictive maintenance, digital twins, quality assurance, and collaborative robots that work safely alongside human workers
- Implementation success depends on data accuracy, breaking down information silos, and workforce training that empowers employees to focus on complex problem-solving
Core Benefits of AI in Manufacturing
Enhancing Operational Efficiency
AI in manufacturing helps companies spot and eliminate production bottlenecks that slow you down. Smart systems that track equipment performance let you optimize your entire workflow from start to finish. Your team can tackle complex tasks while automation handles the repetitive ones.
Production floors with real-time monitoring catch small issues before they become major problems. Process automation streamlines resource allocation and schedule management across your factory. Machines equipped with AI algorithms run simulations of different scenarios, helping you make data-driven decisions.
Companies save valuable time with AI-powered inspection systems that check products faster and more accurately than human inspectors. Smart factories report productivity jumps of up to 50% through automated quality testing. Your manufacturing process flows more smoothly when AI automates repetitive paperwork, freeing staff for more valuable work.
Reducing Costs and Resource Utilization
Benefits of AI in manufacturing include notable cost savings through smarter operations. AI-driven maintenance programs can cut machinery costs by up to 25% and reduce breakdowns by 70%. Production lines waste less material thanks to optimized cutting patterns and improved resource planning.
Energy use drops when intelligent systems monitor consumption in real-time and adjust settings automatically. AI in manufacturing extends beyond production improvements to include smart inventory management that predicts exactly what stock you need, eliminating excess inventory costs.
Early adopters report 15% lower logistics costs and 35% smaller inventory levels through improved supply chain planning. Quality control becomes more effective when AI detects defects earlier, reducing scrap and rework. Digital twins allow you to test changes virtually before implementing them on physical equipment, slashing testing costs.
Companies using these technologies see impressive returns – top performers generate 13% ROI on AI projects according to IBM research, more than double the industry average of 5.9%.
Improving Product Quality and Consistency
Quality control reaches new heights with AI systems that inspect products with up to 90% accuracy in spotting defects. In the manufacturing industry, consistent product quality drives customer satisfaction and cuts warranty claims.
Computer vision technology identifies tiny flaws invisible to human inspectors, maintaining higher standards across your product line. Manufacturing environments become fully visible with AI monitoring that offers a complete view of factories, production lines, and warehouses.
AI in their operations helps companies ensure regulatory compliance by tracking safety protocols and product standards. Quality control automation checks products against precise benchmarks in real-time, maintaining tight tolerances even at high production speeds.
Visual inspection tools verify that labels are correctly placed and readable without halting production. Manufacturers using these technologies report quality improvements of up to 35% through automated inspection processes.

Accelerating Innovation and Time-to-Market
Product design cycles shrink dramatically when you use artificial intelligence to explore multiple options simultaneously. Rather than building physical prototypes for each iteration, designers create virtual models first, saving time and resources.
Companies like GE leverage advancements in AI to analyze a million design variations in just 15 minutes – a task that previously took two full days. Generative AI creates fresh content and design options tailored to specific market needs, helping your engineers explore possibilities faster.
The future of manufacturing involves quick design cycles where teams evaluate multiple options rapidly before selecting the best solution. Technology to create flexible production comes into play with concepts like "factory-in-a-box" that deploy quickly to meet changing market demands.
3D printing supported by intelligent systems ensures proper material use with real-time error correction. Virtual testing through digital models lets you run stress tests before building physical products, cutting development time and costs.
Strengthening Competitive Advantage
AI integration gives you the agility to respond quickly to changing market demands and customer preferences. The manufacturing sector uses AI to enable mass customization without sacrificing efficiency or increasing costs.
Companies that allow manufacturers to gather and analyze production data gain strategic advantages through real-time pattern recognition. Supply chain reliability improves significantly when AI solution implementations reduce forecasting errors by up to 50%.
The benefits AI brings include throughput increases of around 20% compared to companies without these technologies. Manufacturing leaders who adopt these systems gain the flexibility to adapt production lines to individual customer requirements.
The industrial robotics market reached 680,000 units in 2022 and continues growing, projected to hit $150 billion by 2031. AI optimizes supply networks and improves service levels by as much as 65%, giving you an edge over competitors still using traditional methods. Smaller operations can compete effectively with larger companies by reshaping the manufacturing process through improved efficiency and quality.
Critical Manufacturing Applications and Use Cases Driving Benefits
Advanced Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance stands as one of the most valuable applications in manufacturing. This approach combines machine learning with sensor data (temperature, vibration, movement) to forecast equipment failure before it happens.
AI is used to analyze performance patterns and predict precisely when maintenance should occur. Instead of rigid schedules, you can plan work during non-peak hours to minimize disruption. Real-time data from equipment helps catch tiny issues before they cause major breakdowns.
Automotive manufacturers use this technology on assembly robots to prevent costly production stoppages. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, this approach reduces equipment downtime by 35-45%. Technology and infrastructure investments in predictive systems pay off through longer machinery lifespan and more reliable operations.
AI is transforming how companies maintain equipment by establishing normal operating parameters and quickly flagging deviations. Decision-makers use these insights to plan capital investments wisely, knowing exactly when to upgrade or replace machinery. Learn how AI catches small problems that regular maintenance checks might miss, preventing unexpected breakdowns.
Machine Health Monitoring and Digital Twins
Production line efficiency improves when machines have digital counterparts for monitoring and testing. Digital twins create virtual replicas of your equipment, production lines, and even entire factories for simulation and analysis.
AI models combined with deep learning process data from IoT sensors to keep these virtual models updated with live information. Modern manufacturing facilities use these digital replicas to test different operating scenarios without risking physical equipment.
This smart manufacturing approach helps teams monitor operations without directly intervening with hardware. Sensor networks track parameters like temperature, vibration, and performance metrics to build accurate simulations of your equipment.
Real-world examples show how companies use these models to predict exactly how machinery will respond to different production scenarios. The technology uncovers root causes of equipment problems by comparing actual performance against expected parameters. When changes need testing, teams can try them virtually before implementing them physically, reducing operational risks.

Intelligent Quality Assurance Systems
Use cases for intelligent quality systems continue to expand as companies discover their effectiveness. AI technology analyzes products against benchmarks in real-time to maintain consistent quality standards.
Quality assurance adapts quickly when designs change or custom orders require different specifications. AI is the perfect solution for monitoring production data and alerting teams when quality metrics drift outside acceptable ranges.
These systems learn over time, combining data from various sources to predict potential quality issues before they affect production. Every aspect of manufacturing benefits from automated quality control that prevents defective products from reaching customers.
Production lines using these systems track output continuously and notify managers immediately if numbers decrease or flaws appear. Manufacturing include quality data integration with production scheduling to optimize overall processes. Applications of AI in quality control reduce the risk of costly recalls by catching defects early. AI empowers manufacturers to work alongside other technologies like IoT sensors for comprehensive quality monitoring.
Automated Visual Inspection
Computer vision systems used in manufacturing detect defects with remarkable precision by analyzing images or video of products. Manufacturers use AI to identify anomalies and quality deviations that human inspectors might miss.
The automotive industry employs AI tools to examine every millimeter of car surfaces for imperfections. Visual inspection technology eliminates the need for time-consuming and error-prone human checks on high-volume production lines.
Manufacturing is no exception to the trend toward automation of visual quality control. Silicon wafer producers use specialized tools to identify microscopic "killer" defects in microchip production.
AI to automate visual inspection delivers consistent results without human fatigue or variability factors. Artificial intelligence in manufacturing enables real-time inspection feedback to production systems for immediate adjustments. These technologies can simultaneously analyze multiple product features for comprehensive quality assessment.
Supply Chain Intelligence and Optimization
Production process improvements extend beyond the factory floor to encompass entire supply networks. AI analyzes vast datasets to predict demand, manage inventory, and streamline logistics operations.
Manufacturers can use simulation models to predict and prepare for supply disruptions before they happen. Early adopters of this approach report impressive results: 15% lower logistics costs, 35% reduction in inventory levels, and up to 65% improvement in service levels.
AI transforms how companies identify supply chain weaknesses like declining vendor performance or potential material shortages. Manufacturing companies integrate machine learning for demand forecasting and automation of procurement activities.
Order management systems with intelligence capabilities track and optimize fulfillment to ensure timely delivery. Food producers might use these tools to anticipate seasonal demand changes and adjust supply chains accordingly. These systems provide real-time insights into global supply networks to minimize financial losses from disruptions. Companies facing common challenges in logistics find that data-driven predictions enable proactive rather than reactive measures.
Demand Forecasting and Inventory Management
Demand forecasting helps companies anticipate customer needs before they arise. AI algorithms combine historical sales data with external factors like weather, market trends, and economic indicators to create accurate predictions.
Companies analyze data at granular levels to optimize for specific products and locations based on local demand patterns. AI helps manufacturers adapt quickly to market changes through real-time analysis of sales information.
Inventory management powered by artificial intelligence tracks past sales, current stock, and market trends to determine optimal inventory levels. Food producers use these systems to monitor ingredient usage and forecast needs based on production schedules and seasonal factors.
AI can also reduce forecast errors by up to 50% according to McKinsey research. Subset of AI tools maintain appropriate stock levels by predicting demand and adjusting inventory between locations. Benefits and use cases include preventing both overstocking (which ties up capital) and stockouts (which lose sales). Cases for AI in manufacturing often highlight inventory management as a high-ROI application that delivers quick returns.
Collaborative Robots (Cobots) in Production
Automation takes on new forms with collaborative robots designed to work safely alongside your team members. Unlike traditional industrial robots, these machines learn different tasks and navigate around obstacles without requiring fixed programming.
Electronics manufacturers see major efficiency gains when AI and ML power cobots for precise component placement. Car factories use cobots to handle heavy parts while humans secure them in place, combining machine strength with human dexterity.
Visual recognition and learning abilities help these robots perform challenging tasks with remarkable accuracy. Agile manufacturing becomes possible when cobots automate repetitive or error-prone tasks while improving worker safety.
Traditional manufacturing limitations fade when human workers and smart machines collaborate effectively. Use cobots to find and retrieve items in large warehouses, dramatically improving logistics efficiency. These systems represent the next stage in robotic process automation, serving as extra "helping hands" on production lines. They handle potentially dangerous tasks like pouring hot materials, reducing workplace injury risks.
Process Optimization and Automation
AI enhances visibility across operations by identifying inefficiencies and suggesting specific improvements. Companies implement AI to improve processes beyond the factory floor, including administrative and logistical activities.
Robotic arm movements get optimized to minimize unnecessary motion, speeding up assembly while maintaining safety standards. Automated systems handle paperwork tasks like orders, invoices, and reports that previously required manual processing.
Manufacturing include advanced resource allocation systems that automatically schedule tasks and optimize workflows based on multiple factors. Adopting AI for process optimization boosts productivity and profitability through detailed analysis of operations data.
Some companies authorize their systems to make minor improvements autonomously while implementing larger suggested changes after review. AI is transforming how information flows between departments by breaking down silos for integrated operational views. These tools identify subtle patterns in production data that would take human analysts days or weeks to discover.
Measuring the Impact: ROI of AI in Manufacturing
Quantifiable Performance Indicators
According to IBM research, top-performing companies generate 13% ROI on AI system implementations - more than double the industry average of 5.9%. The market value for these technologies continues to grow, projected to reach approximately $20.8 billion by 2028.
Industry growth remains strong, with the AI is the perfect technology market worth about $2.3 billion in 2022 and expected to hit $16.3 billion by 2027, representing a 47.9% compound annual growth rate.
The Manufacturing Leadership Council reports 70% of leaders believe these technologies would greatly benefit at least 31 areas related to business performance. However, only 22% had specific metrics to measure AI's effectiveness despite high expectations.
Companies typically focus AI is transforming on two primary areas first: maintenance (29%) and quality control (27%). Grand View Research attributes strong industry growth to "the escalating demand to manage progressively larger and intricate datasets."
The industrial robot market reached over 680,000 units in 2022 and should grow to $150 billion in value by 2031. A World Economic Forum study found 70% of global manufacturers understand how these technologies generate business value, while 57% already have pilot programs or full deployments underway.
Productivity Gains and Efficiency Metrics
Factories using smart image recognition for quality testing report productivity increases up to 50%. Visual inspection systems achieve up to 90% accuracy in detecting product defects, substantially improving overall quality.
Companies implementing these technologies typically increase production throughput by 20% while improving quality by as much as 35%. Predictive maintenance programs reduce equipment downtime by 35-45% according to U.S. Department of Energy data.
Maintenance costs drop by approximately 10% when companies implement predictive approaches. Material and energy waste decrease while profitability and sustainability improve together.
Supply chain improvements include 15% lower logistics costs, 35% reduction in inventory levels, and up to 65% improvement in service levels for early adopters. Forecasting errors drop by up to 50% compared to traditional methods.
Design teams work faster too - GE engineers now analyze a million design variations in just 15 minutes instead of two days. McKinsey research confirms that predictive maintenance reduces annual maintenance costs by up to 10%.
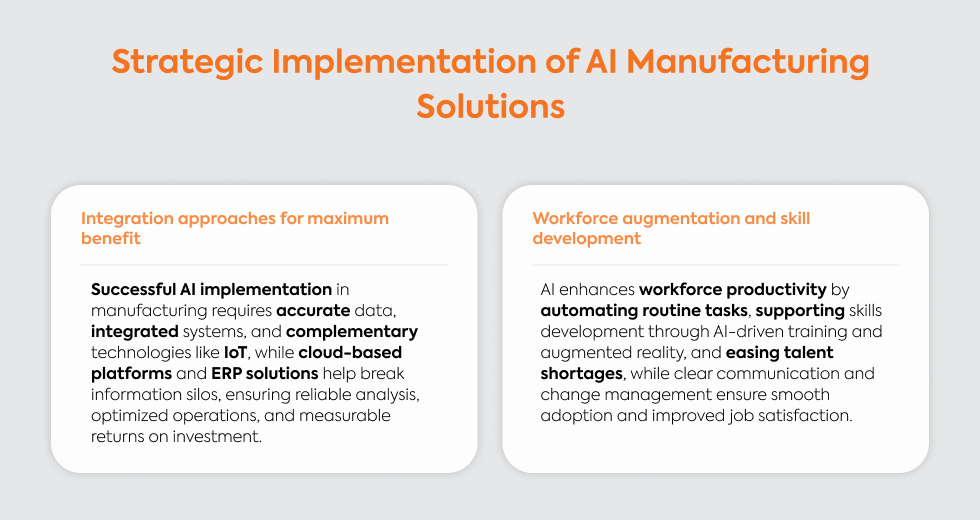
Strategic Implementation of AI Manufacturing Solutions
Integration Approaches for Maximum Benefit
Before starting an AI project, you should audit your data for accuracy and ensure measurement instruments are properly calibrated. Information silos need breaking down before implementation to avoid misleading predictions and recommendations.
Many companies find comprehensive business platforms like ERP software helpful for integrating data across different departments. Cloud-based platforms with built-in AI tools often prove more practical than developing custom AI models internally.
Integration with complementary technologies like IoT devices, augmented reality, and existing ERP systems provides additional valuable data sources. Human oversight and quality control checks remain important to ensure the analysis remains valid and actionable.
The World Economic Forum identifies three major deployment categories that deliver results: operational performance, workforce augmentation, and sustainability initiatives. Targeted implementation strategies help you address specific needs while generating healthy returns on investment.
Cloud solutions like NetSuite for Manufacturing offer centralized views that eliminate information silos. Successful implementation requires solid data foundations and careful planning to maximize effectiveness across your operations.
Workforce Augmentation and Skill Development
AI empowers your workers by handling mundane tasks so they can focus on complex problem-solving and strategic planning. The talent challenge remains significant - 49% of senior decision-makers report struggling to recruit qualified people and retain employees, especially engineering leaders.
Successful programs require experts who understand how to apply these technologies to specific manufacturing challenges. Training programs using AI-driven simulations and augmented reality help workers master complex machinery at their own pace.
Nearly all manufacturing organizations report some impact from automation, making change management strategies essential for smooth transitions. Clear communication about how technologies enhance rather than replace jobs helps ease employee concerns about job security.
Learning curves shorten when new employees and experienced workers use AI-powered support tools that provide immediate feedback. On-the-spot assistance for factory workers helps troubleshoot problems quickly and improves overall performance.
Training programs enhanced with these technologies improve job performance and worker satisfaction while reducing learning time. Augmented reality guided by smart systems overlays instructions onto physical equipment, giving workers hands-free access to information during maintenance and operation tasks.
Ready to Transform Your Manufacturing Operations with AI?
As you've seen, AI offers tremendous potential to optimize your manufacturing processes, reduce costs, and strengthen your competitive advantage. But implementation can be complex, requiring specialized expertise to develop solutions tailored to your specific operational needs.
At Gauss, we specialize in developing custom AI solutions for manufacturing companies like yours. Our team of experts can help you navigate the journey from identifying high-impact AI applications to implementing systems that deliver measurable ROI.
Whether you're looking to implement predictive maintenance, optimize your supply chain, enhance quality control, or explore other AI applications discussed in this article, we have the technical expertise to bring your vision to life.
Don't let implementation challenges prevent you from realizing the benefits of AI in your manufacturing operations.
Contact Gauss today to start a conversation about your specific needs and discover how our custom AI solutions can help you stay ahead of the competition.
