TABLE OF CONTENTS:
- What is a Kanban Board?
- Elements of a Kanban Board
- Kanban Practices
- Advantages of using a Kanban board
- What is a Gantt chart?
- Elements of a Gantt Chart
- Advantages of using a Gantt Chart
You've probably heard about Kanban boards and Gantt charts.
Kanban use has gone from 7% in 2020, to 56% in 2022, most likely due to the global shift to remote work and less workers being in the office.
On the other hand, Gantt charts have a long history and have been prevalent in project management since the 19th century.
So, let us find out what they are really for and how to use them to your advantage.
What is a Kanban Board?
Kanban is a way to organize work, where tasks are shown as cards and moved from one status to another.
As a concept, Kanban was created in the 1940s in Japan, specifically at Toyota headquarters, to improve efficiency and make work processes easier.
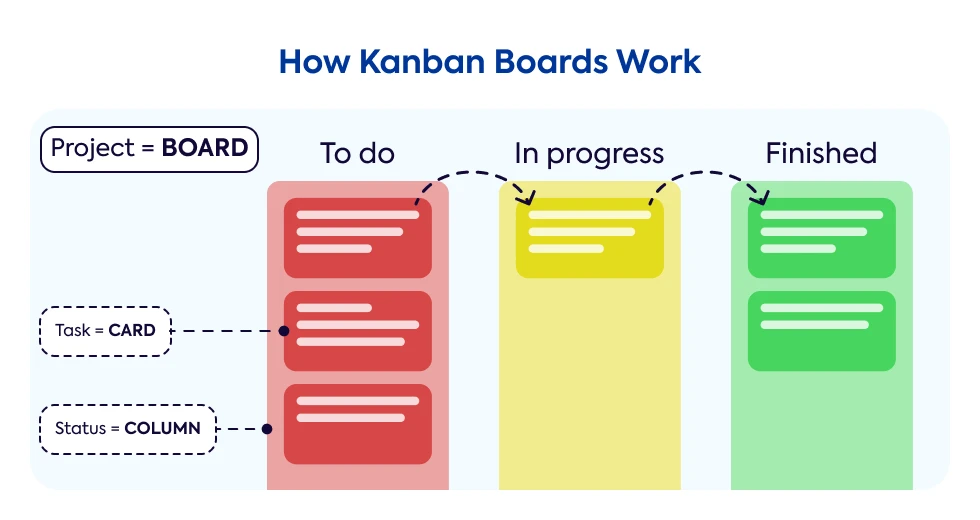
The Kanban board represents a project or workflow and it is made up of columns that define task stages with cards that describe and represent tasks as they get completed.
Elements of a Kanban Board
A Kanban board consists of 3 key elements:
1. Kanban Columns
Columns define workflow phases as cards move from column to column, clearly showing the stage of each task.
A Kanban board is typically divided into 3 main phases:
- Requested tasks or To-do
- Tasks in progress or In progress
- Completed tasks or Finished
But the phase names and their number can be adjusted according to business and project needs.
2. Kanban Cards
Cards represent project tasks or activities and they contain key information such as task description, to-do date, and the person responsible for its completion.
Different colors are often used to easily visualize different task elements such as task type or the responsible team.
3. In-progress Task Limit
Setting a limit on the number of active tasks helps avoid confusion and work overload.
They help team members focus on the tasks that are in progress, while other tasks remain on hold or are already finished.
Better team focus and better organization helps achieve greater efficiency.
Kanban Practices
Kanban practices help achieve better transparency, efficiency, and control over tasks.
There are 6 basic Kanban practices:
Visualizing workflow
Use a board with columns and cards to visualize the work process, where each column represents a task phase, and each card represents a task or activity.
This helps visualize the whole process, helping to check project progress at a glance.
Limiting the number of active tasks
Each card on the board represents a task, making it easy to see the number of tasks in each phase.
By setting limits on the number of tasks allowed in each stage of the workflow, Kanban helps prevent bottlenecks and overloading team members with too many tasks at once.
Managing Work Processes
The whole purpose of the Kanban system is to create a smooth process, so the focus remains on managing and speeding up the task flow.
Easily assigning tasks and changing their work status, helps speed up and optimize workflow.
Setting Clear Rules for Work Processes
By setting clear guidelines, teams better understand task phases and workflow progress.
With a well-defined work policy and task overview, each team member has an easier time self-organizing and understanding the common goal.
Leaving Room for Feedback
Allowing feedback helps identify problems and encourages new ideas within teams.
Companies should be open to changes and promote the exchange of ideas and knowledge among employees.
Continuous Improvement
Using team feedback and analytics, Kanban helps identify improvement opportunities.
By implementing changes to achieve a better and smoother business process, continuous improvement can be achieved.
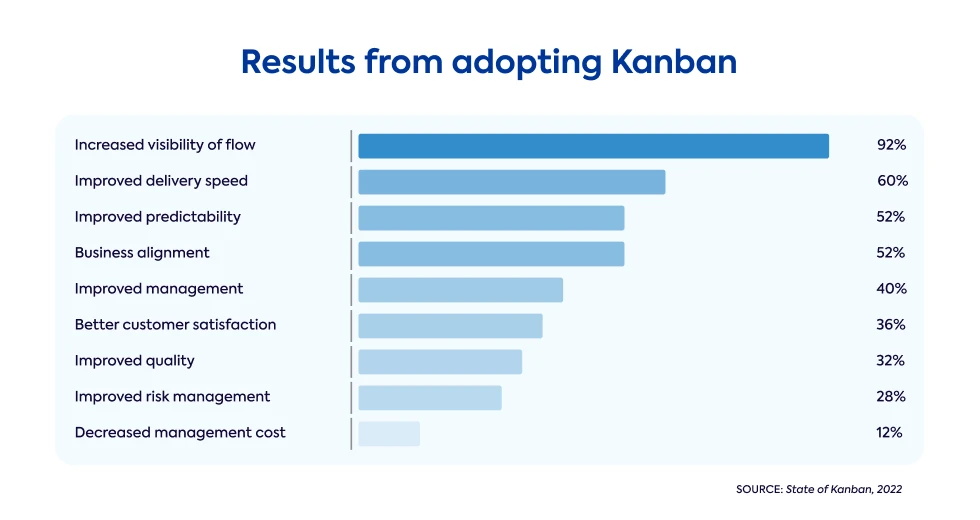
Advantages of using a Kanban board
The advantages of using a Kanban board in the project are:

What is a Gantt chart?
Gantt charts are a tool for visualizing project tasks arranged along a timeline.
After the invention of the Harmonogram by Polish engineer Karol Adamiecki in 1896, Henry Gantt improved the idea and created a chart that was later named after him.
It displays project flow over time by representing tasks or activities as bars along a timeline, indicating when they start, how long they last, and when they end.
This allows teams to track project progress, identify possible delays, and coordinate project segments in order to achieve goals on time.
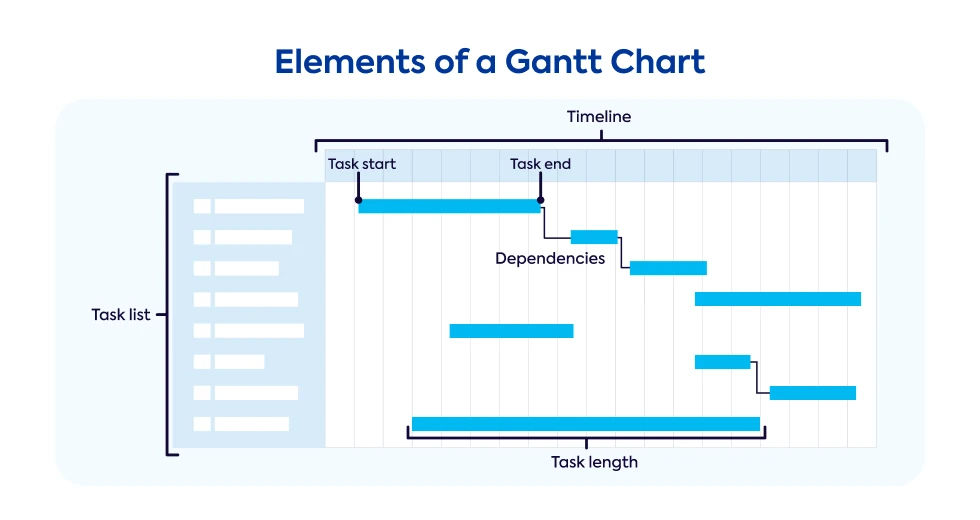
Elements of a Gantt Chart
A Gantt chart consists of 3 main elements:
1. Time
Time is represented at the top of a Gantt chart, usually in months, but other time intervals can be used.
2. Task or activities
Task or activity names are typically displayed on the left side, while their duration is visually represented by the length and position of task bars.
3. Dependencies
Some tasks need to be finished before others can be started, which is represented by arrows that connect dependent task bars.
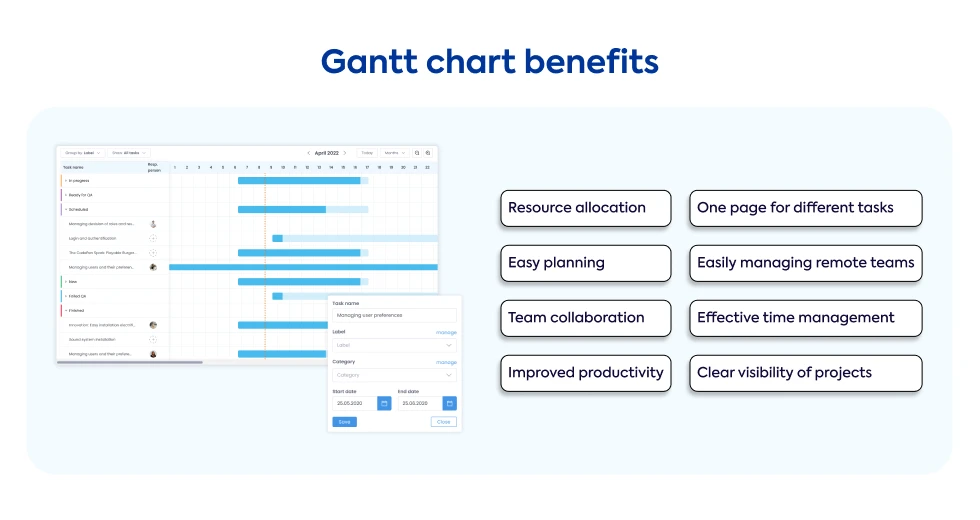
Advantages of using a Gantt Chart
The advantages of using a Gantt chart in your project are:
Kanban boards are great for independent tasks and repetitive actions, especially in agile methodologies, while Gantt charts are more useful for tasks that are interrelated and follow a more traditional waterfall methodology.
You can also combine these tools to get a more detailed picture of the project and easier problem detection.
If you want to make the most of both Kanban boards and Gantt charts in project management, explore our Gauss Box business solution for project management.
